Molluscum contagiosum is a skin rash caused by a virus from the family of pox viruses. The rash has small clear or flesh-colored bumps and these bumps can spread from one part of the body to another or from person to person. Generally, molluscum spots are found on the stomach, face, arms, legs or in the nappy area.
Molluscum contagiosum is the only member of the Molluscipoxvirus genus. The word “molluscum” comes from the Latin “molluscum”, meaning “snail” or “clam”. Despite the word’s origin, humans are the only known hosts of the molluscum contagiosum virus, and we don’t get it from snails or clams.
What Causes Molluscum?
The molluscum virus causes the rash after it enters through a small break in the skin. Bumps usually appear 2–6 weeks after that.
This virus affects young children and people with weakened immune systems or those with allergies and atopic conditions such as asthma. Naturally, without intervention, it usually takes 9-18 months to clear up but can take up to 5 years too.
The molluscum virus is quite contagious and can spread easily from skin touching skin that has bumps. When kids scratch the bumps, the virus goes under their fingernails and easily spreads to other parts of the body. Kids also can get it by touching things that have the virus on them, such as toys, clothing, towels, and bedding. It can last 12 month to 4 years.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Molluscum?
The rash is the telltale sign of molluscum. Its bumps:
- Start as very small spots about the size of a pinhead.
- Grow over a few weeks. They can be as large as a pea or pencil eraser.
- Are soft and smooth and may have a small dent in the center.
- Often are painless, but can get itchy, sore, red, and/or swollen.
- Can get infected with bacteria if kids scratch or pick at them.
- Can appear alone or in groups, or rows. Most people get between 1 and 20 bumps.
- Can show up almost anywhere on the skin except for the palms and soles. In kids, they’re most often on the trunk, arms, and face.
- The virus lives on the skin and once all the bumps are gone, the virus is gone. You can be re-infected if you come in contact with the virus again.
How to prevent
- Avoid close body contact with anyone until all of the molluscum bumps are gone.
- Avoid shaving or scratching the bumps. They can spread to other parts of your body.
- Avoid wearing clothing that can rub against the skin infection and cause more irritation.
- When possible cover the bumps with a bandage to avoid scratching and spreading the virus.
- Do not share towels, clothing, washcloths or other personal items.
- eating a diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthful fats
- seek treatment for nutrient deficiencies, Zinc, Vitamin D, Iron, Vitamin A
- support the immune system as it kills off the virus.
- Try to limit sugar and processed foods by finding a good balance with treats and nutritious snacks.
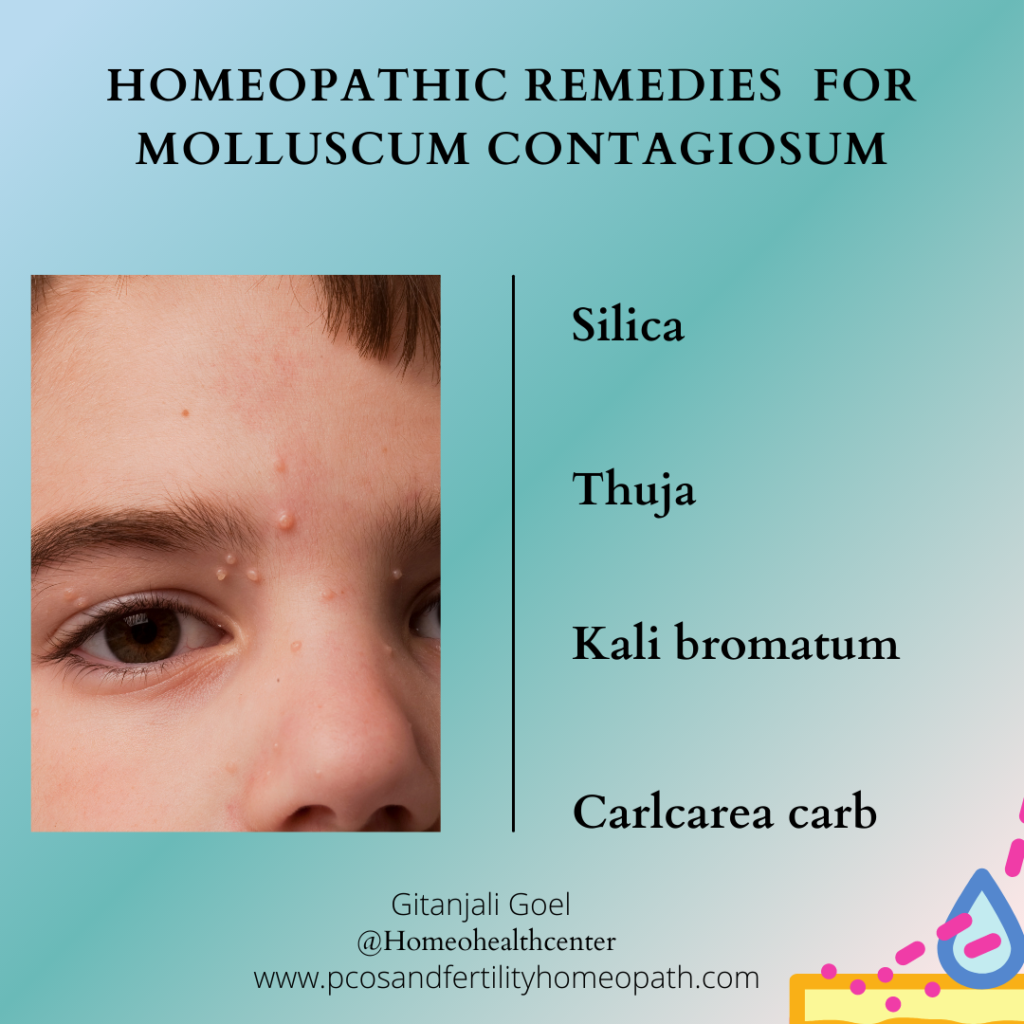
Homeopathic remedies to treat Contagiosum Molluscum
Silica
There are eruptions with offensive pus. Itching only in the daytime and evening. There are cracks at the end of fingers. Painless swelling of glands. Patient is always chilly and wants plenty of warm clothing.
Thuja
Dry skin, with brown spots. Wart-like eruption especially on anogenital region. Perspiration is sweetish and strong. Eruptions only on covered parts and worse after scratching. Left sided and chilly medicine for those who have emotional sensitiveness and fixed ideas.
Kali bromatum
Face flushed. Acne of face, pustules. General failure of mental power, loss of memory, melancholia, anesthesia of the mucous membranes. Suicidal mania with tremulousness. Itching of skin worse on chest, shoulders, and face.
Lycopodium
Wonderful medicine for various skin complaints including molluscum and abscesses. Feels worse from warm applications
Carlcarea carb
Molluscum contagiosum is usually on the face and hands. Skin looks unhealthy and can have ulcers easily as small wounds do not heal readily. Glands are swollen. Feels better in cold air.




